Distributed Performance-portable Stencil Compuitation
What is bricks
Bricks is a data layout and code generation framework, enable performance-portable stencil across a multitude of architectures
- x86 CPUs (AVX2, AVX512)
- ARM CPUs (ASIMD, SVE)
- Intel Knights Landing (AVX512)
- Intel GPUs (OpenCL/Sycl/DPC++)
- OpenCL >= 3.0 with support of cl_khr_subgroup_shuffle_relative
- NVIDIA GPUs (CUDA)
- AMD GPUs (HIP)
Math kernel code and data manipulation code is shared across these platform, while achieving best-in-class performance on all platforms simultaneously. Especially, Brick layout is well suited to higher-order(bigger-wider) stencil computations.
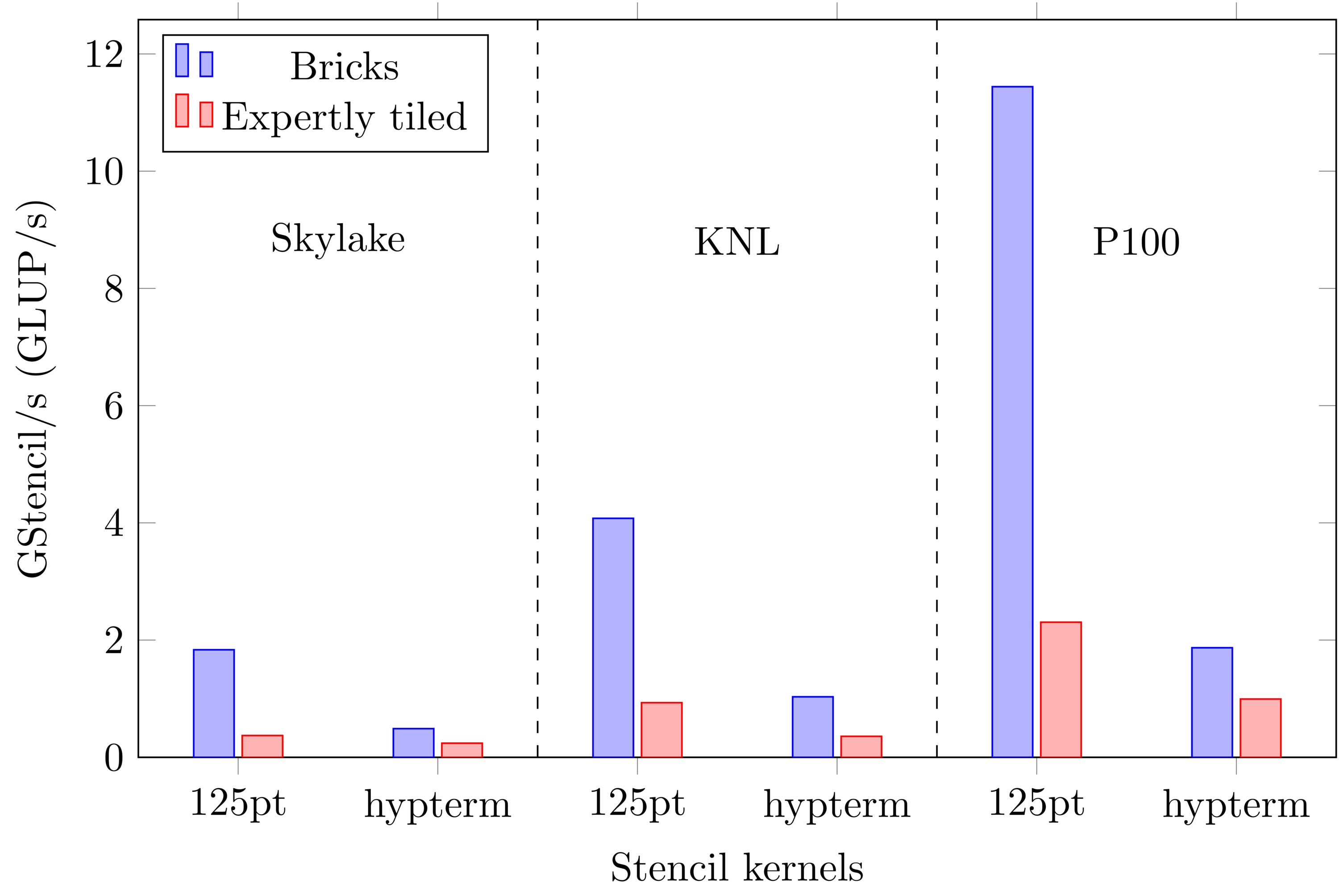
Achieve consistent 1.9x-4.9x speedup across different architectures including Skylake, Intel Knights Landing, and NVidia P100 GPUs
Brick layout is flexible, allows flexible domain shapes and enables fast "ghost cell" data communication with MPI.
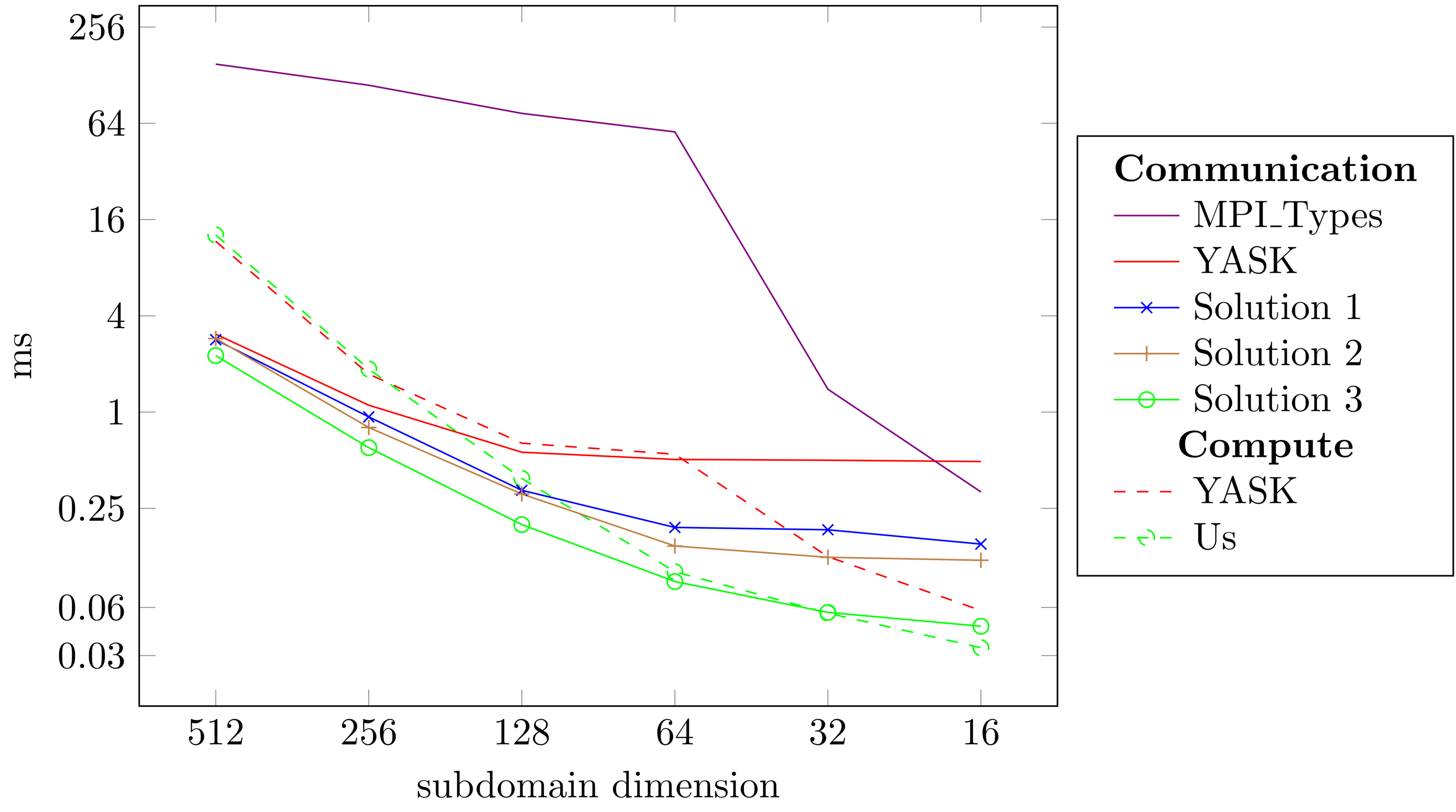
Efficient ghost zone exchange achieves up to 10x faster than state-of-the-art YASK and up to 600x compared to cray-mpich/7.7.10 MPI_Types.
Get the Code
Get code from Github, and start exploring the code documentation.
Acknowledgements
- This research was supported by the Exascale Computing Project (17-SC-20-SC), a joint project of the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science and National Nuclear Security Administration.
- This research used resources of the Oak Ridge Leadership Facility at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, which is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725.
- This research used resources of the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility at Argonne National Laboratory, which is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC02-06CH11357.
- This research used resources in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, which are supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science’s Advanced Scientific Computing Research program under contract number DE-AC02-05CH11231.
Publications
[1] Zhao, Tuowen, Samuel Williams, Mary Hall, and Hans Johansen. 2018. Delivering Performance-Portable Stencil Computations on CPUs and GPUs Using Bricks. In 2018 IEEE/ACM International Workshop on Performance, Portability and Productivity in HPC (P3HPC). 59-70. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1109/P3HPC.2018.00009
[2] Tuowen Zhao, Protonu Basu, Samuel Williams, Mary Hall, and Hans Johansen. 2019. Exploiting reuse and vectorization in blocked stencil computations on CPUs and GPUs. In Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis (SC '19). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 52, 1–44. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1145/3295500.3356210
[3] Tuowen Zhao, Mary Hall, Hans Johansen, and Samuel Williams. 2021. Improving communication by optimizing on-node data movement with data layout. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGPLAN Symposium on Principles and Practice of Parallel Programming (PPoPP '21). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 304–317. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1145/3437801.3441598